Psilocybe Cubensis vs. Amanita Muscaria: A Comparative Exploration of Two Iconic Psychedelic Mushrooms

Psychedelic mushrooms have fascinated humans for centuries, with their potential to induce altered states of consciousness and offer unique spiritual experiences. Among the many species of psychedelic fungi, Psilocybe cubensis and Amanita muscaria stand out as two of the most well-known and widely discussed. In this blog, we’ll delve into the world of these two iconic mushrooms, comparing and contrasting their effects, cultural significance, and historical use.
Psilocybe Cubensis: The Magic Mushroom
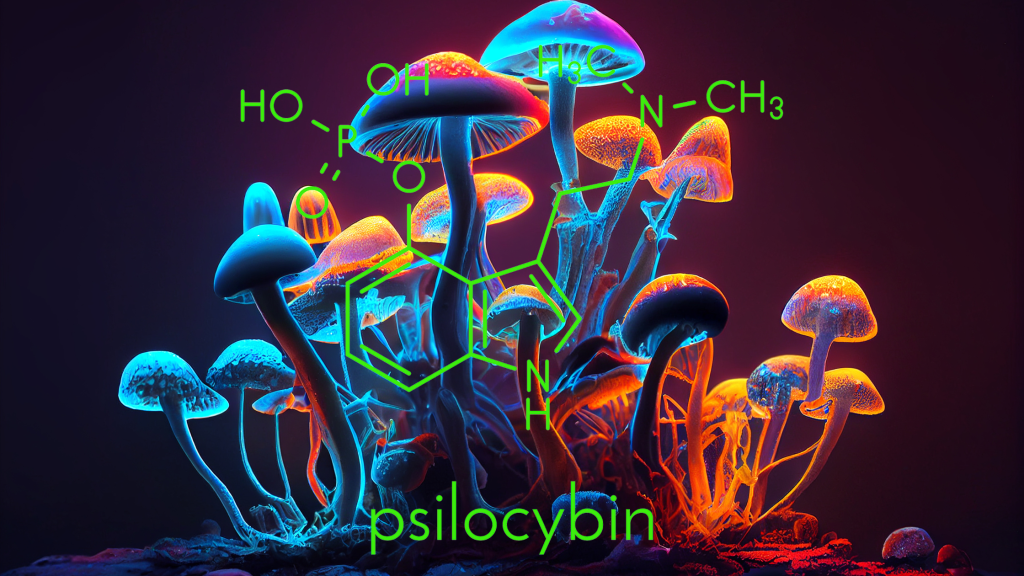
Psilocybe cubensis, commonly known as magic mushrooms, belong to the Psilocybe genus. They are characterized by their small, brownish caps and long, slender stems. These mushrooms contain psychoactive compounds, primarily psilocybin and psilocin, which can induce vivid hallucinations, euphoria, and profound introspection.
Effects:
- Psilocybe cubensis is renowned for its primarily positive and introspective effects. Users often report enhanced creativity, altered perception of time, and increased emotional sensitivity.
- Many people find that Psilocybe cubensis can be an excellent tool for self-discovery and personal growth. It is often used in therapeutic settings to address mental health issues, including depression, anxiety, and PTSD.
Cultural Significance:
- Psilocybe cubensis has been used in traditional and shamanic practices by indigenous cultures in Central and South America for centuries. It is a key component in rituals like the “Velada,” a Mazatec ceremony.
- In the 20th century, Psilocybe cubensis gained popularity in Western counterculture movements, especially during the 1960s and 1970s, contributing to its contemporary significance.
Historical Use:
- Psilocybe cubensis has a rich history of use among various indigenous communities in Mexico, where it is considered sacred and used for divination and healing purposes.
- The discovery of Psilocybe cubensis by Western scientists in the mid-20th century spurred a resurgence of interest in psychedelic research.
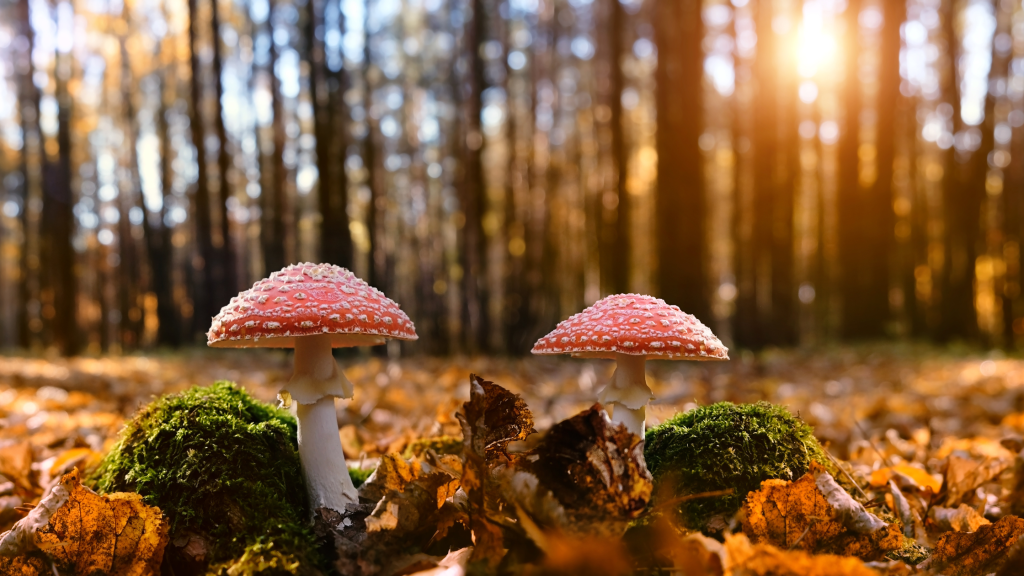
Amanita Muscaria: The Fly Agaric
Amanita muscaria, also known as the fly agaric, is instantly recognizable with its bright red cap adorned with white spots. It’s infamous for its association with fairy tales and folklore, as well as its use by indigenous Siberian tribes in shamanic practices.
Effects:
- Amanita muscaria contains muscimol and ibotenic acid, which induce unique effects quite distinct from Psilocybe cubensis. Its experience can be highly unpredictable, with users reporting both euphoric and delirious states.
- The effects of Amanita muscaria may include dream-like visions, out-of-body experiences, and a sense of disconnection from reality.
Cultural Significance:
- Amanita muscaria is famously depicted in various European fairy tales and folklore, where it is associated with magical and mystical qualities.
- Siberian shamans have a long history of using Amanita muscaria in their rituals to communicate with spirits and gain insights.
Historical Use:
- The use of Amanita muscaria in Siberian shamanism dates back centuries. It was considered a means to connect with the spirit world and receive guidance.
- Unlike Psilocybe cubensis, Amanita muscaria has limited historical use in Western cultures and has only recently gained attention in psychedelic circles.
Comparison: Cubensis vs. Amanita
Psilocybe cubensis and Amanita muscaria represent two different facets of the psychedelic mushroom world. While both are revered for their unique properties and have contributed to human culture and spirituality, they offer contrasting experiences.
Psilocybe cubensis is known for its introspective, emotionally positive effects, making it popular in contemporary Western psychedelic therapy and personal development. Its use has deep historical roots in indigenous cultures, particularly in the Americas.
Amanita muscaria, with its enigmatic and dream-like qualities, is more aligned with folklore, fairy tales, and shamanic traditions. Its effects can be unpredictable and sometimes challenging, which might explain its limited historical use outside of Siberia.
Ultimately, the choice between Psilocybe cubensis and Amanita muscaria depends on personal preferences and the desired psychedelic experience. Whether one seeks introspection, healing, or mystical encounters, both mushrooms offer a window into the profound and diverse world of psychedelics. However, it is crucial to approach these substances with respect, caution, and, when possible, under the guidance of experienced individuals or professionals, due to their potential for unpredictable effects.